Roman Chair Knee Raise 101 Video Tutorial
0
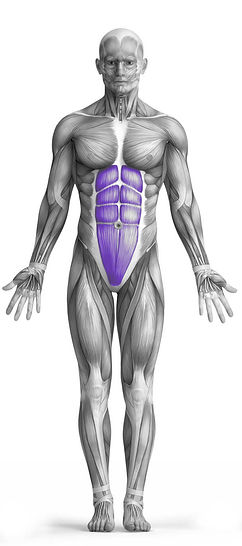
Exercise Synopsis
Target Muscle Group
Abs
Secondary Targets
None
Execution
Compound
Force Type
N/A
Required Equipment
Bodyweight
Fitness Level
Beginner
Variations
None
Alternatives
None
Timer
Hour
Minute
Second
Stopwatch
00:00:00:00
Overview
The Roman Chair Knee Raise is an effective bodyweight exercise that primarily targets the abdominal muscles. Performed on a Roman chair or a similar bench, the movement involves lifting the knees towards the chest while maintaining a stable upper body. This exercise engages the core throughout the motion, promoting strength and endurance in the abs. Since no additional equipment is required beyond bodyweight, it's a convenient exercise for both beginners and more advanced individuals looking to strengthen their midsection. Proper form is essential to maximize the benefits and avoid unnecessary strain on the lower back.
How to Perform
Begin by positioning yourself on the Roman chair, ensuring that your forearms are supported by the pads and your back is comfortably against the backrest. Grip the handles firmly for stability.
Lift your legs off the footrests, allowing them to hang straight down with your body fully supported.
Engage your core and, with control, bring your knees up towards your chest, aiming to raise them as high as you can while maintaining a steady upper body.
Once you reach the peak of the movement, hold for a brief moment to fully engage the abdominal muscles.
Slowly lower your knees back down to the starting position, ensuring that the movement is controlled to maximize the effectiveness of the exercise.
Continue for the desired number of repetitions, focusing on smooth, deliberate movements to prevent swinging and to engage the abs throughout.
Tips
Perform the Roman chair knee raise at a slow, controlled pace to ensure maximum activation of the abdominal muscles. Rushing through the movement or relying on momentum will reduce the focus on your abs.
To increase the challenge, you can add weight by holding a dumbbell between your feet while executing the exercise, which will intensify the resistance and further engage your core.
How Not to Perform
Avoid Using Momentum: Do not swing your legs or use your body’s momentum to lift your knees. Focus on controlled, smooth movements to ensure that the effort is coming from your abs rather than relying on any external force.
Keep Your Back Stable: Do not arch your lower back or lean forward excessively. Maintain a neutral spine and engage your core throughout the movement to avoid straining your back.
Do Not Rush: Avoid performing the exercise too quickly. Moving at a fast pace takes the emphasis off your abs and reduces the effectiveness of the exercise. Slow down to maximize abdominal engagement.
Do Not Let Your Feet Touch the Footrest: When lowering your legs, do not let your feet rest on the footrests between reps. Keeping your legs slightly off the rests will maintain tension in the abdominal muscles and prevent unnecessary rest.
Avoid Overextending Your Legs: Do not let your legs hang too low or extend too far down, as this can lead to poor posture and unnecessary strain on your lower back. Keep your legs in a controlled, slightly bent position when lowering them.
Focus on Abdominal Engagement: Ensure that you are initiating the movement with your core, not your hip flexors. Avoid using your legs to pull yourself up; the focus should remain on the abdominal muscles.
Don’t Hold Your Breath: Remember to breathe steadily throughout the exercise. Holding your breath can increase tension in your body and reduce the effectiveness of the movement.
Do Not Use Excessive Weight (if adding weight): If you’re using added weight, avoid using too much resistance at once. Start with a manageable weight and gradually increase it to ensure proper form and prevent injury.
Variations
Variations of fitness exercises refer to different ways of performing a specific exercise or movement to target various muscle groups, intensities, or goals. These variations aim to challenge the body differently, prevent plateaus, and cater to individuals with varying fitness levels.
Alternatives
Alternative exercises in fitness refer to different movements or activities that target similar muscle groups or serve the same training purpose as the primary exercise. These alternative exercises can be used as substitutes when the original exercise is unavailable or challenging to perform due to various reasons such as equipment limitations, injuries, or personal preferences.



