Straight-Legged Hip Raise 101 Video Tutorial
0
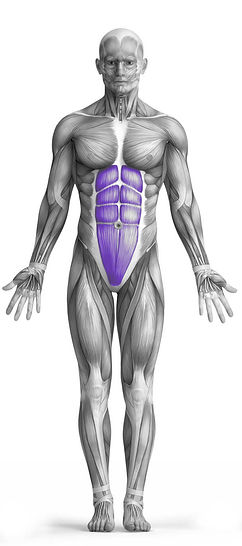
Exercise Synopsis
Target Muscle Group
Abs
Secondary Targets
Execution
Isolation
Force Type
Core
Required Equipment
Dumbbell
Fitness Level
Intermediate
Variations
None
Alternatives
None
Timer
Hour
Minute
Second
Stopwatch
00:00:00:00
Overview
The Straight-Legged Hip Raise is a bodyweight exercise that primarily targets the abdominal muscles with secondary engagement of the lower back. In this exercise, the individual lies flat on their back with legs extended straight upwards towards the ceiling. Using the core muscles, they lift their hips off the floor, aiming to create a straight line from shoulders to feet. The movement primarily involves hip flexion and extension, effectively engaging the abs to stabilize the pelvis and spine. While the main focus is on the abs, the lower back muscles are also activated to support the spine throughout the movement. This exercise requires no equipment, making it accessible for individuals of all fitness levels, and can be incorporated into core strengthening routines to improve abdominal strength and stability.
How to Perform
Setup: Begin by lying flat on your back on a mat or exercise surface with your legs fully extended and your arms resting comfortably by your sides.
Engage Core: Activate your abdominal muscles by gently pulling your belly button towards your spine. This will help stabilize your pelvis and protect your lower back throughout the exercise.
Leg Positioning: Extend your legs straight up towards the ceiling, keeping them together and your toes pointed. This is your starting position.
Hip Raise: Inhale deeply, then exhale as you lift your hips off the ground towards the ceiling. Focus on using your abdominal muscles to initiate the movement, rather than relying solely on momentum.
Controlled Movement: Lift your hips until your body forms a straight line from shoulders to heels, with your legs perpendicular to the floor. Avoid arching your lower back excessively by maintaining tension in your core muscles.
Pause and Squeeze: At the top of the movement, pause for a moment and squeeze your abdominal muscles to maximize engagement. This will help to further strengthen and tone your abs.
Lowering Phase: In a controlled manner, slowly lower your hips back down to the starting position, keeping your core engaged throughout the descent. Avoid letting your legs drop too quickly or bouncing off the floor.
Repeat: Complete the desired number of repetitions, aiming for smooth and controlled movements with each repetition. Focus on maintaining proper form and technique throughout the exercise.
Breathing: Remember to coordinate your breathing with the movement. Inhale as you lower your hips towards the floor, and exhale as you lift your hips back up towards the ceiling.
Adjustments and Progressions: If you find the exercise too challenging, you can bend your knees slightly or place your hands under your hips for additional support. As you become stronger, you can increase the difficulty by holding a dumbbell between your feet or extending your legs further away from your body.
Tips
Begin by lying flat on your back with legs extended straight up towards the ceiling, arms by your sides.
Engage your core muscles by drawing your belly button towards your spine to stabilize your pelvis.
Lift your hips off the ground towards the ceiling, focusing on using your abs to initiate the movement.
Aim to create a straight line from shoulders to heels, with legs perpendicular to the floor.
Squeeze your abs at the top of the movement to maximize engagement and control.
Lower your hips back down to the starting position in a slow and controlled manner, keeping your core engaged.
Avoid arching your lower back excessively by maintaining tension in your abs throughout the exercise.
Coordinate your breathing by inhaling as you lower your hips and exhaling as you lift them.
Ensure your legs remain straight and your toes pointed throughout the movement for optimal muscle engagement.
Adjust the difficulty by bending your knees slightly or holding a dumbbell between your feet as you become stronger.
How Not to Perform
Avoid Using Momentum: Refrain from swinging your legs or using momentum to lift your hips off the ground. This diminishes the effectiveness of the exercise and places unnecessary strain on the lower back.
Do Not Arch Your Back: Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement by avoiding excessive arching of the lower back. This helps to prevent injury and ensures proper engagement of the abdominal muscles.
Avoid Lifting Hips Too High: Lift your hips only as high as you can while maintaining control and stability. Lifting excessively high can lead to hyperextension of the lower back and may strain the muscles.
Do Not Let Legs Drift: Keep your legs perpendicular to the floor and avoid letting them drift towards your head or away from your body. This ensures proper alignment and maximizes engagement of the abs.
Avoid Holding Your Breath: Remember to breathe continuously throughout the exercise to maintain oxygen flow to the muscles. Holding your breath can increase intra-abdominal pressure and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
Do Not Neglect Core Engagement: Focus on actively engaging your core muscles throughout the movement. Neglecting core engagement can lead to compensatory movements and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
Avoid Rapid Movements: Perform the exercise in a slow and controlled manner to maximize muscle engagement and reduce the risk of injury. Avoid rapid or jerky movements that can compromise form.
Do Not Overextend: Avoid overextending your legs or hips at the top of the movement. This can strain the lower back and shift the focus away from the abs.
Do Not Rush: Take your time with each repetition and focus on quality over quantity. Rushing through the exercise can lead to poor form and reduce its effectiveness.
Avoid Neglecting Lower Back: While the primary focus is on the abs, do not neglect the engagement of the lower back muscles. Maintain a balanced contraction throughout the movement to support spinal stability.
Variations
Variations of fitness exercises refer to different ways of performing a specific exercise or movement to target various muscle groups, intensities, or goals. These variations aim to challenge the body differently, prevent plateaus, and cater to individuals with varying fitness levels.
Alternatives
Alternative exercises in fitness refer to different movements or activities that target similar muscle groups or serve the same training purpose as the primary exercise. These alternative exercises can be used as substitutes when the original exercise is unavailable or challenging to perform due to various reasons such as equipment limitations, injuries, or personal preferences.



