Alternating High Knee Raise 101 Video Tutorial
0
Timer
Hour
Minute
Second
Stopwatch
00:00:00:00
Overview
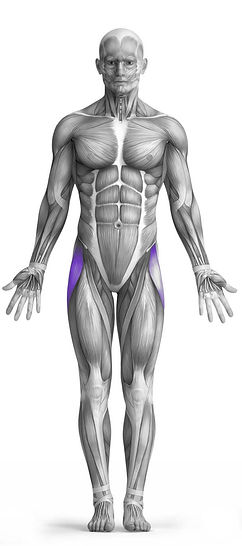
The Alternating High Knee Raise is an effective bodyweight exercise primarily targeting the hip flexors while also engaging the abs and obliques as secondary muscle groups. This exercise involves lifting one knee at a time towards your chest in a controlled, alternating manner. It is excellent for enhancing hip flexor strength and improving core stability. As a bodyweight exercise, it requires no additional equipment, making it a convenient choice for both home workouts and fitness routines at the gym. The movement helps in improving coordination, balance, and overall lower body strength.
How to Perform
Starting Position: Stand upright with your feet hip-width apart, engaging your core muscles. Ensure one foot is securely planted on the ground.
Knee Raise: Lift one knee towards your chest until your thigh is parallel to the ground. Keep your torso stable and avoid any twisting of the hips during this movement.
Pause and Return: Hold the raised position for a brief moment, then lower your leg back to the starting position with control.
Alternate Legs: Repeat the movement with the opposite leg while maintaining your balance and stability throughout the exercise.
Repetition: Continue alternating legs for the desired number of repetitions, ensuring each lift is smooth and deliberate.
★ Bonus: For exercises that involve external weights (such as dumbbells, barbells, or machines), the One Rep Max (1RM) calculator can help you estimate your maximum lifting capacity. Use it to track your strength progress and adjust your training for optimal results.
Tips
Engage Core: Keep your core muscles tight to maintain balance and stability.
Straight Posture: Stand upright with your back straight and shoulders relaxed.
Controlled Movements: Lift each knee slowly and deliberately to maximize muscle engagement.
No Hip Twisting: Avoid twisting your hips during the knee lift to ensure effective targeting of the hip flexors.
Hold Briefly: Pause for a moment at the top of each knee raise for better muscle activation.
Alternate Legs: Perform the exercise by alternating legs, ensuring smooth transitions between each lift.
No Equipment Needed: This exercise requires only your body weight, making it suitable for any setting.
How Not to Perform
Avoid Leaning Back: Do not lean backward or arch your lower back, as this can strain your lower back and reduce the effectiveness of the exercise. Keep your torso upright.
Prevent Hip Twisting: Do not let your hips twist or rotate during the knee lift. Focus on keeping your hips stable to effectively target the hip flexors.
Don’t Rush the Movement: Avoid performing the exercise too quickly. Fast movements can lead to poor form and less muscle engagement. Maintain a steady and controlled pace.
No Excessive Momentum: Refrain from using excessive momentum to lift your knees. Instead, rely on your hip flexors and core muscles to perform the lift.
Avoid Overextending the Knee: Do not raise your knee too high to the point where it causes discomfort. Aim for a parallel position to the ground for optimal engagement.
Do Not Forget to Breathe: Remember to breathe steadily throughout the exercise. Holding your breath can cause unnecessary tension and reduce your exercise efficiency.
Neglecting Core Engagement: Ensure that you actively engage your core muscles throughout the movement. This helps in stabilizing your body and enhancing the effectiveness of the exercise.
Ignoring Form: Avoid performing the exercise with poor form or without paying attention to technique. Proper form is crucial for preventing injuries and achieving the desired muscle activation.
Inadequate Rest Between Sets: Do not skip resting between sets. Allow adequate recovery to maintain proper form and avoid fatigue-related mistakes.
Avoid Using Hands for Balance: Do not use your hands for support or balance. Keep your arms relaxed by your sides to fully engage your core and hip flexors.
Variations
Variations of fitness exercises refer to different ways of performing a specific exercise or movement to target various muscle groups, intensities, or goals. These variations aim to challenge the body differently, prevent plateaus, and cater to individuals with varying fitness levels.
Alternatives
Alternative exercises in fitness refer to different movements or activities that target similar muscle groups or serve the same training purpose as the primary exercise. These alternative exercises can be used as substitutes when the original exercise is unavailable or challenging to perform due to various reasons such as equipment limitations, injuries, or personal preferences.








