Seated High Cable Row 101 Video Tutorial
0
Timer
Hour
Minute
Second
Stopwatch
00:00:00:00
Overview
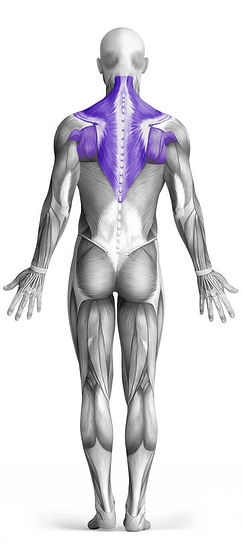
The Seated High Cable Row is an effective upper back exercise that primarily targets the upper back muscles while also engaging the biceps and lats as secondary muscles. Utilizing a cable machine, this exercise involves pulling a high-placed cable attachment towards your torso while maintaining a seated position. The movement emphasizes the contraction of the upper back muscles, promoting strength and stability in this area. Proper form is essential to maximize the benefits and reduce the risk of injury, making it a valuable addition to any upper body workout routine.
How to Perform
Set Up Your Equipment: Begin by positioning a flat bench in front of a cable machine. Attach a rope handle to the low pulley of the machine and select a weight that matches your fitness level.
Sit Properly: Take a seat on the bench, facing the cable machine. Ensure that your feet and knees are together, planted firmly on the ground for stability.
Grip the Rope: Reach forward and grasp the rope handle with a neutral grip (palms facing inward, thumbs pointing towards each other). Sit upright, keeping your shoulders back, chest out, and your arms fully extended. This will be your starting position.
Engage Your Core: Engage your core muscles to stabilize your torso, ensuring that your back remains straight throughout the movement.
Perform the Row: Slowly pull the rope towards your upper chest, leading the movement with your elbows. As you pull, keep your shoulders down and squeeze your upper back muscles (particularly your traps and lats).
Part the Rope: As you reach the peak of the movement, slightly separate the rope handles so that your hands come close to your shoulders. This additional motion enhances the contraction in your upper back and traps.
Pause and Control the Descent: Hold the position briefly at the top of the movement, feeling the squeeze in your upper back. Then, slowly reverse the motion, lowering the rope back to the starting position with control.
Repeat: Complete the desired number of repetitions, maintaining good form throughout each rep to maximize the effectiveness of the exercise and minimize the risk of injury.
Tips
Contract Your Shoulder Blades: As you reach the peak of the movement, focus on drawing your shoulder blades together, ensuring a strong contraction in your upper back.
Isolate Arm Movement: Keep your body stable throughout the exercise. Only your arms should be moving during the row, while your torso, shoulders, and legs remain steady and engaged to avoid unnecessary movement.
How Not to Perform
Avoid Using Excessive Weight: Don’t select a weight that’s too heavy, as this can cause you to use improper form or engage other muscle groups excessively. Choose a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with control and correct technique.
Don’t Use Momentum: Avoid jerking or swinging your body to pull the cable. This can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and increase the risk of injury. Focus on a controlled, smooth movement.
Don’t Overextend Your Arms: Ensure that your arms are fully extended at the starting position, but avoid hyperextending them. Overextending can put unnecessary strain on your shoulders and wrists.
Avoid Leaning Back: Keep your torso upright and avoid leaning back during the row. Leaning can shift the focus away from the upper back and place strain on your lower back. Maintain a neutral spine and engaged core throughout the exercise.
Don’t Let Your Shoulders Hunch: Keep your shoulders down and back throughout the movement. Allowing your shoulders to hunch up towards your ears reduces the engagement of your upper back muscles and can lead to shoulder strain.
Avoid Flaring Your Elbows Out: Keep your elbows close to your body as you pull the cable. Flaring your elbows out can shift the emphasis away from your upper back and increase the risk of shoulder injuries.
Don’t Rush the Movement: Perform each repetition slowly and with control. Rushing through the exercise can lead to poor form and decreased muscle engagement.
Avoid Inconsistent Breathing: Maintain a steady breathing pattern. Holding your breath or breathing irregularly can affect your performance and stability. Inhale as you return to the starting position and exhale as you pull the cable towards you.
Don’t Neglect Warm-Up: Ensure you are properly warmed up before starting the exercise. Skipping a warm-up can lead to stiffness and increased risk of injury.
Avoid Over-Reliance on Hands: Focus on engaging your back muscles rather than just pulling with your hands. This helps in maximizing the effectiveness of the exercise and minimizes stress on your arms.
Variations
Variations of fitness exercises refer to different ways of performing a specific exercise or movement to target various muscle groups, intensities, or goals. These variations aim to challenge the body differently, prevent plateaus, and cater to individuals with varying fitness levels.
Alternatives
Alternative exercises in fitness refer to different movements or activities that target similar muscle groups or serve the same training purpose as the primary exercise. These alternative exercises can be used as substitutes when the original exercise is unavailable or challenging to perform due to various reasons such as equipment limitations, injuries, or personal preferences.



